Permanent impairment
If a worker is left with a permanent impairment as a result of a work related injury or illness, there is a provision under the Return to Work Act 1986 for a lump sum payment to be paid in respect of that permanent impairment.
Permanent impairment entitlements are for a temporary or permanent bodily or mental abnormality or loss caused by an injury for which the insurer/self-insurer has accepted liability.
For example, if a worker has an accepted claim for a knee injury following a workplace incident and later appears to have developed a secondary psychological injury due to the same incident, the insurer must accept liability for the psychological injury for a permanent impairment assessment to occur.
A permanent impairment assessment can only be done once the injury has reached maximum medical improvement. This is considered to occur when the worker's condition is well stabilised and is unlikely to change substantially in the next year with or without medical treatment.
Payment to the worker may be made to compensate for the permanent impairment once the injury has reached maximum medical improvement. This payment does not affect the workers’ rights to weekly compensation benefits, medical or rehabilitation expenses.
Assessment procedure
| NOTE: if a worker arranges their own assessment, the assessment report and the invoice must be provided to the employer's insurer so they can meet their legislative requirements |
|---|
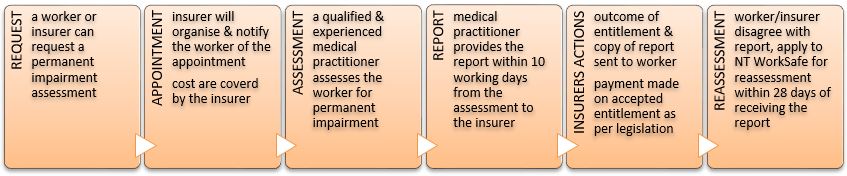
If a worker believes that they have a permanent impairment, they may apply to their employer's insurance company or their own doctor for an assessment of that impairment. If the worker arranges his or her own assessment, the assessment must be sent to the employer's insurer.
Permanent impairment means an impairment or impairments assessed, in accordance with the guides approved and published by the Authority, as being an impairment, or combination of impairments, of not less than 5% of the whole person.
The approved guides used for all assessments are the NT WorkSafe Guidelines for the Evaluation of Permanent Impairment. These guides adopt the 'American Medical Association Guides to the Evaluation of Permanent Impairment (fifth edition)'.
If a worker or the insurer is dissatisfied with the assessed level of permanent impairment, either may apply to NT WorkSafe for a reassessment.
Such applications must be in writing. NT WorkSafe must receive an application for reassessment form must accompany your letter. This must be provided to NT WorkSafe within 28 days of the insurer, or worker, being notified of the initial assessment.
Video Resources
The below video has been developed to give helpful information about workers compensation:
Related Forms and Resources
| Bulletins |
|---|
| Medical practitioners guide to permanent impairment assessment |
| Permanent impairment entitlement |
| Checklists |
|---|
| Permanent impairment assessment checklist for medical practitioners |
| Forms |
|---|
| Application for permanent impairment reassessment |
| Guides |
|---|
| NT WorkSafe guidelines for the evaluation of permanent impairment |